Introduction
There’s been a major flood in Riverbend City. Although the worst of the flood is over, citizens and emergency management professionals are still grappling with the aftermath and consequences, as well as the possibility of additional hazards.
You are an emergency management graduate student at Beck University in Riverbend City, and the city has hired you to help with the flood effort. You have been asked to investigate the situation using the vulnerability hazard model—including root causes, dynamic pressures, unsafe conditions, and hazards. In the coming weeks, you will also be asked to investigate the flood further by applying various theoretical lenses.
Best of luck!
Begin Activity
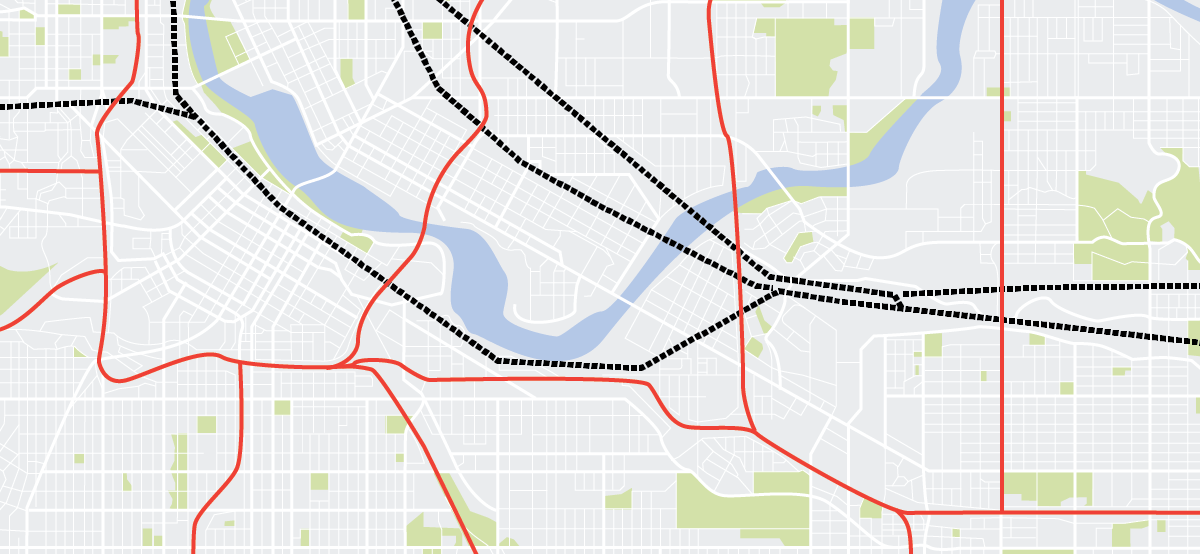
This is Riverbend City.
Last week, after a month of heavy rain, the Brown Trout River flooded.
Click on the highlighted locations to learn more about the vulnerability hazard model—and how this relates to the impact of the flood in two city neighborhoods.
Unit 2
Functionalism
What is functionalism?
Functionalism is a theoretical lens that focuses on how the different parts of society contribute to the stability of the social order. Functionalism sees society as an organism, and societal institutions (like education, the media, government, religion, and family) all serve a role in keeping the organism functioning.
One way to conduct a functionalist analysis of the flood in Riverbend City would be to evaluate how well the institutions in town functioned together to maintain the social order.
Click each location to find out how city institutions function together to keep order, both during and after the flood.
Unit 3
Conflict Theory
What is conflict theory?
Conflict theory is a theoretical lens that focuses on struggles within society. Typically, it focuses on power struggles involving marginalized groups or societal inequalities. According to conflict theory, tensions and conflicts in a society result in the unequal distribution of resources within a community.
One way to conduct a conflict analysis of the flood in Riverbend City would be to investigate and evaluate conflicts resulting from the flood—especially conflicts that relate to power struggles over resources.
Click each location in the Ruby Lake neighborhood to learn more.
Unit 4
Structuralism
What is structuralism?
Structuralism is a way of looking at the world that posits that elements of human culture cannot be understood without looking at the structure of society as a whole. In a way, structuralism is the opposite of individualism; instead of looking at people’s behaviors in a vacuum, structuralism posits that we cannot understand an individual’s behavior without looking at this individual’s relationship to societal structures.
A structuralist analysis might look at how an individual’s experience relates to societal structures as a whole.
Marisol Nunez
Marisol Nunez, 18, has been arrested for looting. She broke into a flooded drug store and tried to steal diapers and cash. From a structuralist perspective, we cannot understand Marisol’s actions without looking at how she functions as an individual, but also as a part of societal structures.
- Marisol had a baby at age 16. She lives in a neighborhood that has one of the highest teen pregnancy rates in the city. Her high school had an abstinence-only sex education program because the largely Catholic community demanded it.
- Marisol had a baby at age 16. She lives in a neighborhood that has one of the highest teen pregnancy rates in the city. Her high school had an abstinence-only sex education program because the largely Catholic community demanded it.
- Marisol is a high school dropout. She could have stayed in school after her baby was born. But the majority of people in her circle are not well educated—especially the women—so this was not a priority for her.
- The father of Marisol’s baby was arrested recently for selling drugs. There are over twice as many Hispanic men in prison as white men in the United States.
- Hispanic women in the United States make about 55 cents for every dollar that a white man makes. Twenty-three percent of the Hispanics live below the poverty line, compared to 10 percent of whites. Twenty-two percent of Hispanics have encountered workplace discrimination, versus only six percent of whites.
Unit 5
Application of Theories of Vulnerability, Risk, and Communication
What are theories of vulnerability, risk, and communication?
These theories examine the ways that we communicate within our social structure, and how these patterns of communication impact our perceptions of risk and vulnerability. Effective communication is absolutely essential during an emergency, and when devising a communication plan, it’s essential to consider carefully the norms and structures of the populations in question.
Click each location to see some of the communication problems during the Riverbend City flood that put people at risk.
Unit 6
Social Constructionist Theory
What is social constructionist theory?
Social constructionist theory is a philosophical lens for thinking about society. It posits that culture, society, and perhaps even reality itself are socially produced, as opposed to naturally determined. Our ideas about what is normal and real are jointly constructed by being part of a society. For example, there is nothing inherently feminine about the color pink or masculine about the color blue, and yet as a society, we have constructed those as the norms for denoting gender, especially when buying a baby gift. Whenever someone declares that something is “just the way it is,” there’s a good chance they’re talking about a social construct.
A social constructionist analysis of a disaster might look at the assumptions that people make that are widely considered to be “true”—but that are actually social constructs.
Click on each location in Riverbend City to see statements that reflect socially constructed myths.
Unit 7
Systems Thinking
What is systems thinking?
Systems thinking is a kind of analysis that is based on how a society or a community’s parts are part of interrelated systems. Systems thinking helps us to better understand society because it helps us understand the parts holistically, as part of interrelated systems. It helps us to make better policy decisions by encouraging us to look beyond the surface level of an incident—and to look at systemic solutions.
Systems thinking can be applied to disaster management by looking at how systems work together to contribute to problems—and how systems can come together to solve them.
InstructionsTBD
Unit 8
Organizational Behavior Theory
What is organizational behavior theory?
Organizational behavior theory is a category of theories that focuses on the structure, process, and design of organizations. In relation to emergency management, organizational theories can be used to investigate the effectiveness of emergency management organizations. It can also be used to assist with business continuity when disaster strikes.
Click on each location in Riverbend City to see what kinds of organizational behavior studies might be conducted on each of these organizations after the emergency is over.
Unit 9
Emergent Behavior Theory
What is emergent behavior theory?
Emergent behavioral theory is a category of theories that focus on the impact that events have on human behavior. Understanding human behavior in relation to emergency management—and not relying on myths—is essential for understanding how best to help people and organizations during and after an emergency.
Click on each location in Riverbend City to see what kinds of emergent behavior studies might be conducted on each of these organizations after the emergency is over.
Unit 10
Development Theories
What are development theories?
Development theories are a category of theories that examine a region’s growth and progress in areas such as economic productivity, sustainability, and social development. The term “development” is typically used when looking at less affluent countries, but can also be used when looking at neighborhoods or cities. Regions that are poorly developed are often at higher risk during an emergency due to increased vulnerability, and may take longer to recover.
One way to conduct a developmental analysis of the flood in Riverbend City would be to evaluate the level of development in an impoverished neighborhood and examine how this contributed to flood damage and other problems.
Click on each location to learn more.
Conclusion
You have completed the Riverbend City: Post-Flood Vulnerabilities activity. This piece provided you with a background for understanding and applying the Vulnerability Hazard Model to a flood in Riverbend City, and also demonstrated how to apply various theoretical lenses to this incident. You will be referring to this piece throughout your program.
























The Police Department helped people evacuate in an orderly way. During a previous disaster, we learned that we had to do a better job of evacuating people who did not own vehicles—so this time, we were in constant communication with the Riverbend City Transit System to make sure there were enough buses on hand to get people to shelters. In my neighborhood, officers did a great job helping a nursing home evacuate its residents—which can be dangerous, but they managed to move all the residents without any injuries. In addition, the police helped maintain order for the people in the city who did not evacuate. Thankfully, looting has been minimal, but we’ve done our best to patrol the neighborhoods. We’ve also tried to check in on residents to make sure they have what they need, and we’ve provided people with information about available resources.
Joanna Penny
Police Captain